Quantized Convolution Fusion Patterns#
Overview#
oneDNN supports both floating-point and quantized Convolution fusion patterns to optimize performance and reduce memory bandwidth requirements. This document describes the supported quantized fusion patterns for Convolution. For floating-point Convolution fusion patterns, refer to Convolution Fusion Patterns for more details.
Pattern Structure#
oneDNN defines quantized Convolution fusion patterns as follows. The blue nodes are required when defining a quantized Convolution fusion pattern while the brown nodes are optional.
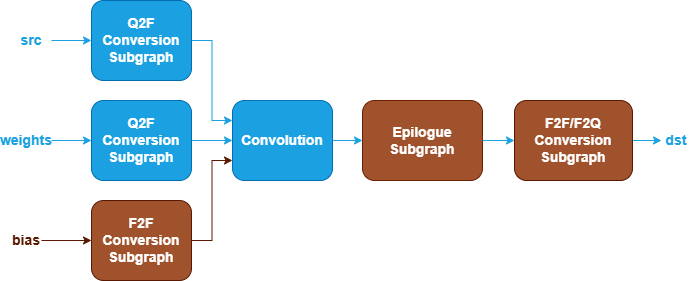
Q2F Conversion Subgraph : Converts
srcandweightstensors from quantized to floating-point. It can be one of the following subgraphs, while the last two subgraphs apply only toweights. See Dequantize, TypeCast and Quantize operations in Graph API.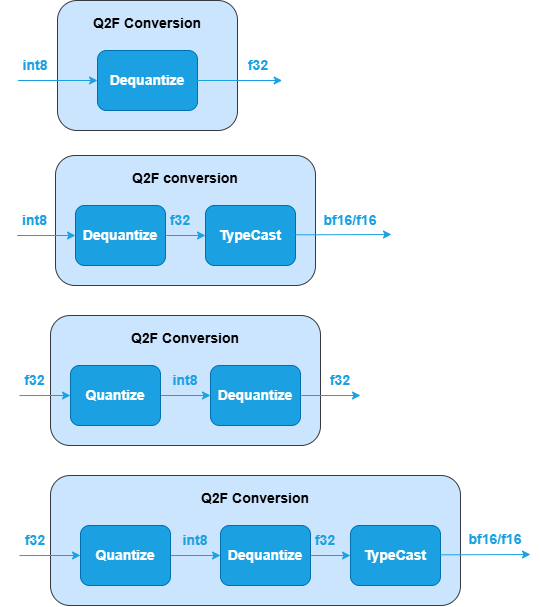
F2F Conversion Subgraph : Converts
biastensor from floating-point to another floating-point. It is constructed by a TypeCast operation.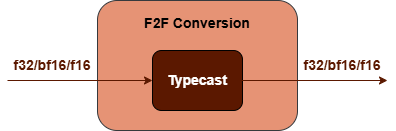
Convolution Operation : Performs convolution between the
srcandweightstensors. Thebiastensor is optional. See the Convolution operation in the Graph API for more details.Epilogue Subgraph : Optional and can include the following operations:
BiasAdd operation.
Binary and Unary operations: refer to the Note in Fusion Patterns.
Combination Rules:
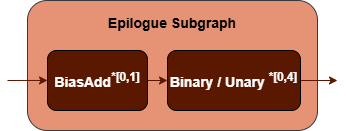
BiasAdd : If present, must be the first op in the epilogue subgraph and can only appear once.
N=20, 0 to 20 Binary or Unary operations are supported in the epilogue subgraph.
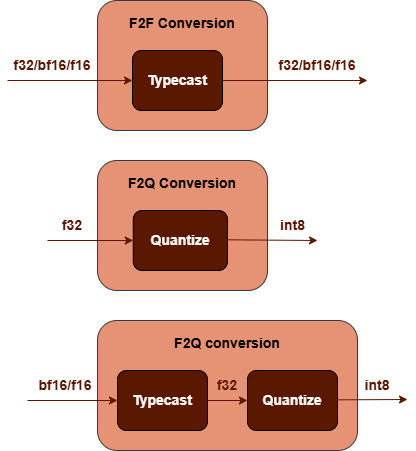
F2F/F2Q Conversion Subgraph : Converts the output tensor from floating-point to floating-point or quantized data type. It can be one of the following subgraphs. See TypeCast and Quantize operations in Graph API.
Data Types#
oneDNN supports the following combinations of data types for src, weights, bias and dst:
src |
weights |
bias |
dst |
|---|---|---|---|
u8,s8 |
s8,f32 |
f32,bf16,f16 |
u8,s8,bf16,f16,f32 |
The definition of the data types and support status on different CPU and GPU platforms follow the general description in the Data Types Guide.
Implementation Limitations#
F2Q Conversion Subgraph used for
dsttensor only supports bf16 to f32 data type conversion.
Implementation Notes#
Post-binary Add operations in the epilogue subgraph support in-place operations when the post-binary Add is the last operation in the epilogue subgraph and the dst output shape is identical and data type size is the same as the binary Add input. In case of an in-place operation, the original input data will be overwritten. Use in-place operations whenever possible for performance.
Example#
oneDNN provides a quantized Convolution example demonstrating how to construct a typical quantized Convolution pattern with oneDNN Graph API on CPU.
