Pool Fusion Patterns#
Overview#
The Pool category includes operations such as: AvgPool and MaxPool.
oneDNN supports various pool fusion patterns to optimize performance and reduce memory bandwidth requirements. This document describes the supported fusion patterns for Pool operations.
Pattern Structure#
oneDNN defines floating-point Pool fusion patterns as follows. The blue nodes are required when defining a Pool fusion pattern while the brown nodes are optional.
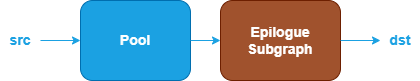
Pool Operation : Performs the corresponding pool operation for the
srctensor. See the AvgPool and MaxPool operations in the Graph API for more details.Epilogue Subgraph : Optional and can include the following operations:
Binary and Unary operations: refer to the Note in Fusion Patterns.
Combination Rules:

N=20, 0 to 20 Binary or Unary operations are supported in the epilogue subgraph.
Data Types#
oneDNN supports the following combinations of data types for src and dst:
src |
dst |
|---|---|
f32,bf16,f16 |
f32,bf16,f16 |
The definition of the data types and support status on different CPU and GPU platforms follow the general description in the Data Types Guide.
Implementation Limitations#
The AvgPool operation doesn’t support the combination of rounding_type equal to ceil and exclude_pad equal to false.
Implementation Notes#
Post-binary Add operations in the epilogue subgraph support in-place operations when the post-binary Add is the last operation in the epilogue subgraph and the dst output shape is identical and data type size is the same as the binary Add input. In case of an in-place operation, the original input data will be overwritten. Use in-place operations whenever possible for performance.
